class Hpdf::Page
- Hpdf::Page
- Reference
- Object
Overview
The page handle is used to operate an individual page.
When Doc#add_page or Doc#insert_page is invoked, a page object
is created.
Included Modules
Direct Known Subclasses
Defined in:
hpdf/page.crConstructors
Instance Method Summary
-
#arc(x : Number, y : Number, ray : Number, ang1 : Number, ang2 : Number)
appends a circle to the current path.
-
#begin_text
begins a text object and sets the current text position to the point (0, 0).
-
#build(&)
build enables DSL style access to building a page
-
#char_space : Float32
gets the current value of the page's character spacing.
-
#char_space=(value : Number)
sets the character spacing for text showing.
-
#circle(x : Number, y : Number, ray : Number)
appends a circle to the current path.
-
#clip
#clipmodifies the current clipping path by intersecting it with the current path using the nonzero winding number rule. -
#close_path
appends a strait line from the current point to the start point of sub path.
-
#close_path_eofill_stroke
closes the current path, fills the current path using the even-odd rule, then it paints the path.
-
#close_path_fill_stroke
closes the current path, fills the current path using the nonzero winding number rule, then it paints the path.
-
#close_path_stroke
closes the current path, then it paints the path.
-
#cmyk_fill : CMYK
returns the current value of the page's filling color.
-
#cmyk_stroke : CMYK
returns the current value of the page's stroking color.
-
#concat(a : Number, b : Number, c : Number, d : Number, x : Number, y : Number)
concatenates the page's current transformation matrix and specified matrix.
-
#context(&)
saves the current graphic state and restores it after the block is completed
-
#create_destination : Destination
creates a new destination object for the page.
-
#create_link_annotation(rect : Rectangle, dst : Destination) : LinkAnnotation
creates a new link annotation object for the page.
-
#create_text_annotation(rect : Rectangle, text : String | Bytes, encoder : Encoder | Nil = nil) : TextAnnotation
creates a new text annotation object for the page.
-
#create_uri_link_annotation(rect : Rectangle, uri : String)
creates a new web link annotation object for the page.
-
#current_font : Font | Nil
gets the handle of the page's current font.
-
#current_font_size : Float32
gets the size of the page's current font.
-
#current_pos : Point
gets the current position for path painting.
-
#current_text_pos : Point
gets the current position for text showing.
-
#curve_to(x1 : Number, y1 : Number, x2 : Number, y2 : Number, x3 : Number, y3 : Number)
appends a Bézier curve to the current path using two specified points.
-
#curve_to(p1 : Point, p2 : Point, p3 : Point)
see
#curve_to -
#curve_to2(x1 : Number, y1 : Number, x2 : Number, y2 : Number)
appends a Bézier curve to the current path using two spesified points.
-
#curve_to2(p1 : Point, p2 : Point)
see
#curve_to2 -
#curve_to3(x1 : Number, y1 : Number, x2 : Number, y2 : Number)
appends a Bézier curve to the current path using two spesified points.
-
#curve_to3(p1 : Point, p2 : Point)
see
#curve_to3 -
#dash
gets the current pattern of the page.
-
#dpi=(dpi : Number)
change the DPI of the page using
#concat -
#draw_image(image : Image, x : Number, y : Number, width : Number, height : Number)
shows an image in one operation.
-
#draw_image(image : Image, rect : Rectangle)
see
#draw_image. -
#draw_rectangle(x : Number, y : Number, w : Number, h : Number, *, line_width lw : Number = 1)
draws a rectangle with the given coordinates and linw width
-
#draw_rectangle(rect : Rectangle, *, line_width lw = 1)
draws a rectangle with the given rectangle and linw width
-
#end_path
ends the path object without filling and painting operation.
-
#eoclip
#clipmodifies the current clipping path by intersecting it with the current path using the even-odd rule. -
#eofill
fills the current path using the even-odd rule.
-
#eofill_stroke
fills the current path using the even-odd rule, then it paints the path.
-
#execute_x_object(image : Image)
draws the XObject using the current graphics context.
-
#fill
fills the current path using the nonzero winding number rule.
-
#fill_stroke
fills the current path using the nonzero winding number rule, then it paints the path.
-
#filling_color_space : ColorSpace
returns the current value of the page's stroking color space.
-
#flat : Float32
gets the current value of the page's flatness.
-
#font : Hpdf::Font?
get the current font if any
-
#g_mode
see
#graphics_mode. -
#g_restore
restore the graphics state which is saved by
#g_save. -
#g_save
saves the page's current graphics parameter to the stack.
-
#g_state_depth : Int32
returns the number of the page's graphics state stack.
-
#graphics_mode : GMode
gets the current graphics mode.
-
#gray_fill : Float32
returns the current value of the page's filling color.
-
#gray_fill=(value : Number)
sets the filling color.
-
#gray_stroke : Float32
returns the current value of the page's stroking color.
-
#gray_stroke=(value : Number)
sets the stroking color.
-
#height : Int32
gets the height of a page.
-
#height=(h : Number)
changes the height of a page.
-
#horizontal_scaling : Float32
returns the current value of the page's horizontal scaling for text showing.
-
#horizontal_scalling=(value : Number)
sets the horizontal scalling for text showing.
-
#line_cap : LineCap
gets the current line cap style of the page.
-
#line_cap=(line_cap : LineCap)
sets the shape to be used at the ends of line.
-
#line_join : LineJoin
gets the current line join style of the page
-
#line_join=(line_join : LineJoin)
Sets the line join style in the page.
-
#line_to(x : Number, y : Number)
appends a path from the current point to the specified point.
-
#line_to(p : Point)
see
#line_to -
#line_width : Float32
gets the current line width of the page.
-
#line_width=(line_width : Number)
sets the width of the line used to stroke a path.
-
#measure_text(text : String | Bytes, *, width : Number, word_wrap : Bool = true) : MeasuredText
calculates the byte length which can be included within the specified width.
-
#measure_text_width(text : String | Bytes) : MeasuredText
measures the passed text width using the current font and font size.
-
#miter_limit : Float32
gets the current value of the page's miter limit.
- #miter_limit=(limit : Number)
-
#move_text_pos(x : Number, y : Number)
moves the current text position to the start of the next line with using specified offset values.
-
#move_to(x : Number, y : Number)
starts a new subpath and move the current point for drawing path,
#move_tosets the start point for the path to the point (x, y) and changes the graphics mode toGMode::PathObject. -
#move_to(p : Point)
see
#move_to -
#move_to_next_line
moves the current text position to the start of the next line.
-
#page_move_text_pos2(x : Number, y : Number)
changes the current text position, using the specified offset values.
-
#path(x : Number, y : Number, &)
create path at given coordinates and yields the block closes the path at the end and returns the result of the block
-
#rectangle(x : Number, y : Number, w : Number, h : Number)
appends a rectangle to the current path.
-
#rectangle(r : Rectangle)
see
#rectangle - #reset_dash!
-
#rgb_fill : RGB
returns the current value of the page's filling color.
-
#rgb_stroke : RGB
returns the current value of the page's stroking color.
-
#rotate=(angle : Number)
sets rotation angle of the page.
-
#set_cmyk_fill(c : Number, m : Number, y : Number, k : Number)
sets the filling color.
-
#set_cmyk_stroke(c : Number, m : Number, y : Number, k : Number)
sets the stroking color.
-
#set_dash(pattern : Array(Number), *, phase = 0)
Sets the line dash pattern in the page.
-
#set_font_and_size(font : Hpdf::Font, size : Number)
sets the type of font and size leading.
-
#set_font_and_size(font : String, size : Number)
see
#set_font_and_size. -
#set_rgb_fill(r : Number, g : Number, b : Number)
sets the filling color.
-
#set_rgb_stroke(r : Number, g : Number, b : Number)
sets the stroking color.
-
#set_size(size : PageSizes, direction : PageDirection = PageDirection::Portrait)
changes the size and direction of a page to a predefined size.
-
#set_slide_show(style : TransitionStyle, disp_time : Number, trans_time : Number = 1)
configures the setting for slide transition of the page.
-
#set_text_matrix(a : Number, b : Number, c : Number, d : Number, x : Number, y : Number)
#set_text_matrixsets a transformation matrix for text to be drawn in using#show_text. -
#show_text(text : String | Bytes)
prints the text at the current position on the page.
-
#show_text_next_line(text : String | Bytes)
moves the current text position to the start of the next line, then prints the text at the current position on the page.
-
#show_text_next_line_ex(text : String | Bytes, word_space : Number, char_space : Number)
moves the current text position to the start of the next line, then sets the word spacing, character spacing and prints the text at the current position on the page.
-
#stroke
paints the current path.
-
#stroking_color_space : ColorSpace
returns the current value of the page's stroking color space.
-
#table(rect : Rectangle, line_width lw : Number = 1, spacing sp : Number = 0, fixed_row_height fwh : Number = 0, &)
table creates a table at the given rect and yields the block in the context of the created table.
-
#table(*, x : Number, y : Number, width : Number, height : Number, line_width lw : Number = 1, fixed_row_height fwh : Number = 0, spacing sp : Number = 0, &)
table creates a table at the given coordinates and yields the block in the context of the created table.
- #text(name = nil, size = nil, *, encoding enc : String | Nil = nil, &)
-
#text_end
ends a text object.
-
#text_leading=(value : Number)
sets the text leading (line spacing) for text showing.
-
#text_out(x : Number | Symbol, y : Number | Symbol, text : String | Bytes)
prints the text on the specified position.
-
#text_rect(left : Number, top : Number, right : Number, bottom : Number, text : String | Bytes, *, align : TextAlignment = TextAlignment::Left) : Number
print the text inside the specified region.
-
#text_rect(rect : Rectangle, text : String | Bytes, *, align : TextAlignment = TextAlignment::Left) : Number
see
#text_rect. -
#text_rendering_mode : TextRenderingMode
returns the current text rendering mode.
-
#text_rendering_mode=(mode : TextRenderingMode)
sets the text rendering mode.
-
#text_rise : Float32
returns the current value of the page's text rising.
-
#text_rise=(value : Number)
moves the text position in vertical direction by the amount of
value. -
#text_width(text : String | Bytes) : Float32
gets the width of the text in current fontsize, character spacing and word spacing.
- #to_unsafe : LibHaru::Page
-
#trans_matrix : TransMatrix
gets the current transformation matrix of the page.
- #use_font(name, size, *, encoding : String | Nil = nil)
-
#width : Int32
gets the width of a page.
-
#width=(w : Number)
changes the width of a page.
-
#word_space : Float32
returns the current value of the page's word spacing.
-
#word_space=(value : Number)
sets the word spacing for text showing.
Instance methods inherited from module Hpdf::Helper
bool(val : Bool) : Int32
bool,
nilable_str(v : Pointer(UInt8)) : String | Nil
nilable_str,
real(val : Number) : LibHaru::Real
real,
uint(val : Number) : LibHaru::UInt
uint,
uint16(val : Number) : UInt16
uint16
Constructor Detail
Instance Method Detail
appends a circle to the current path.
An application can invoke #arc when the #graphics_mode of the
page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::PathObject.
- x, y the center point of the circle.
- ray the ray of the circle.
- ang1 the angle of the begining of the arc.
- ang2 the angle of the end of the arc. It must be greater than ang1.
begins a text object and sets the current text position to
the point (0, 0). An application can invoke #begin_text when
the graphics mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription.
And it changes the graphics mode to GMode::TextObject.
sets the character spacing for text showing.
The initial value of character spacing is 0.
An application can invoke #char_space= when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- value the value of character spacing.
appends a circle to the current path.
An application can invoke #circle when the #graphics_mode of the
page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::PathObject.
- x, y the center point of the circle.
- ray the ray of the circle.
#clip modifies the current clipping path by intersecting
it with the current path using the nonzero winding number
rule. The clipping path is only modified after the succeeding
painting operator. To avoid painting the current path, use
the function #end_path.
Following painting operations will only affect the regions of
the page contained by the clipping path. Initially, the
clipping path includes the entire page. There is no way to
enlarge the current clipping path, or to replace the clipping
path with a new one. The functions #g_save and #g_restore
may be used to save and restore the current graphics state,
including the clipping path.
appends a strait line from the current point to the start point
of sub path. The current point is moved to the start point of sub
path. An application can invoke #close_path when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PathObject.
closes the current path, fills the current path using the
even-odd rule, then it paints the path. An application can
invoke #close_path_eofill_stroke when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::PathObject or GMode::ClippingPath. And it changes the
graphics mode to GMode::PageDescription.
closes the current path, fills the current path using the
nonzero winding number rule, then it paints the path.
An application can invoke #close_path_fill_stroke when the
graphics mode of the page is in GMode::PathObject or GMode::ClippingPath. And it
changes the graphics mode to GMode::PageDescription.
closes the current path, then it paints the path.
An application can invoke #close_path_stroke when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PathObject or GMode::ClippingPath. And it changes the
graphics mode to GMode::PageDescription.
returns the current value of the page's filling color. #cmyk_fill is
valid only when the page's filling color space is ColorSpace::DeviceCmyk.
returns the current value of the page's stroking color. #cmyk_stroke is
valid only when the page's stroking color space is ColorSpace::DeviceCmyk.
concatenates the page's current transformation matrix and specified
matrix. For example, if you want to rotate the coordinate system of the
page by 45 degrees, use #concat as like demonstrated in the rotate method.
An application can invoke #concat when the #graphics_mode of the
page is in GMode::PageDescription.
Example to change the dpi using concat
concat 72 / dpi, 0, 0, 72 / dpi, 0, 0Example rotate 45 degrees
rad1 = degree / 180 * Math::PI
context do
concat Math.cos(rad1), Math.sin(rad1), -Math.sin(rad1),
Math.cos(rad1), 0, 0
text Hpdf::Base14::Helvetica, 70 do
text_out 100, 100, "Hello World"
end
endcreates a new link annotation object for the page.
- rect a rectangle of clickable area.
- dst a handle of destination object to jump to.
creates a new text annotation object for the page.
- rect a rectangle where the annotation is displayed
- text the text to be displayed.
- encoder an encoder handle which is used to encode the text. If it is null, PDFDocEncoding is used.
creates a new web link annotation object for the page.
- rect a rectangle of clickable area.
- uri URL of destination to jump to.
gets the size of the page's current font. It returns the size of the page's current font. Otherwise it returns 0.
gets the current position for path painting. It returns a Point
struct indicating the current position for path painting of the page.
Otherwise it returns a Point struct of {0, 0}.
An application can invoke #current_pos only when graphics mode is GMode::PathObject.
gets the current position for text showing. It returns a Point struct
indicating the current position for text showing of the page.
Otherwise it returns a Point struct of {0, 0}.
An application can invoke #current_text_pos only when graphics
mode is GMode::TextObject.
appends a Bézier curve to the current path using two specified points.
The point (x1, y1) and the point (x2, y2) are used as the control
points for a Bézier curve and current point is moved to the point
(x3, y3). An application can invoke #curve_to when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PathObject.
- x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 the control points for a Bézier curve.
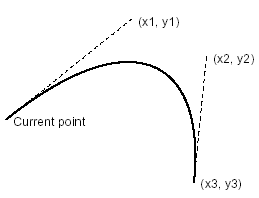
appends a Bézier curve to the current path using two spesified points.
The current point and the point (x2, y2) are used as the control
points for a Bézier curve and current point is moved to the point
(x3, y3). An application can invoke #curve_to2 when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PathObject.
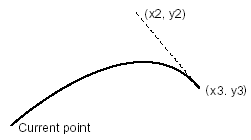
appends a Bézier curve to the current path using two spesified points.
The point (x1, y1) and the point (x3, y3) are used as the control
points for a Bézier curve and current point is moved to the point
(x3, y3). An application can invoke #curve_to3 when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PathObject.

gets the current pattern of the page. First argument is the pattern, second is the phase.
shows an image in one operation.
An application can invoke #draw_image when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::PageDescription.
- image the image object.
- x, y the lower-left point of the region where image is displayed.
- width the width of the region where image is displayed.
- height the width of the region where image is displayed.
draws a rectangle with the given coordinates and linw width
draws a rectangle with the given rectangle and linw width
ends the path object without filling and painting operation.
An application can invoke #end_path when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::PathObject or GMode::ClippingPath. And it changes the
graphics mode to GMode::PageDescription.
#clip modifies the current clipping path by intersecting it
with the current path using the even-odd rule. The clipping
path is only modified after the succeeding painting operator.
To avoid painting the current path, use the function #end_path.
Following painting operations will only affect the regions of
the page contained by the clipping path. Initially, the
clipping path includes the entire page. There is no way to
enlarge the current clipping path, or to replace the clipping
path with a new one. The functions #g_save and #g_restore
may be used to save and restore the current graphics state,
including the clipping path.
HPDF_Page_Clip() modifies the current clipping path by intersecting it with the current path using the even-odd rule. The clipping path is only modified after the succeeding painting operator. To avoid painting the current path, use the function HPDF_Page_EndPath().
fills the current path using the even-odd rule.
An application can invoke #eofill when the #graphics_mode of the
page is in GMode::PathObject or GMode::ClippingPath. And it changes the graphics mode
to GMode::PageDescription.
fills the current path using the even-odd rule, then it paints
the path. An application can invoke #eofill_stroke when the
graphics mode of the page is in GMode::PathObject or GMode::ClippingPath. And it
changes the graphics mode to GMode::PageDescription.
draws the XObject using the current graphics context. This is used
by #draw_image to draw the Image by first calling #g_save and
#concat and then calling #g_restore after #execute_x_object.
It could be used manually to rotate an image.
fills the current path using the nonzero winding number rule.
An application can invoke #fill when the #graphics_mode of thepage is inGMode::PathObjectorGMode::ClippingPath. And it changes the graphics mode toGMode::PageDescription`.
fills the current path using the nonzero winding number rule,
then it paints the path. An application can invoke #fill_stroke
when the #graphics_mode of the page is in GMode::PathObject or GMode::ClippingPath.
And it changes the graphics mode to GMode::PageDescription.
returns the current value of the page's stroking color space.
restore the graphics state which is saved by #g_save.
An application can invoke #g_save when the #graphics_mode of the
page is in GMode::PageDescription.
saves the page's current graphics parameter to the stack.
An application can invoke #g_save up to 28 and can restore the
saved parameter by invoking #g_restore, when the #graphics_mode of
the page is in GMode::PageDescription.
returns the current value of the page's filling color. #gray_fill is
valid only when the page's stroking color space is ColorSpace::DeviceGray.
sets the filling color.
An application can invoke #gray_fill= when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- value the value of the gray level between 0 and 1.
returns the current value of the page's stroking color. #gray_fill is
valid only when the page's stroking color space is ColorSpace::DeviceGray.
sets the stroking color.
An application can invoke #gray_stroke= when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- value the value of the gray level between 0 and 1.
changes the height of a page.
- h Specify the new height of a page. The valid value is between 3 and 14400.
returns the current value of the page's horizontal scaling for text showing.
sets the horizontal scalling for text showing.
The initial value of horizontal scalling is 100.
An application can invoke #horizontal_scalling= when the
graphics mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or
GMode::TextObject.
sets the shape to be used at the ends of line.
An application can invoke #line_cap= when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- line_cap the style of line-cap.
Sets the line join style in the page.
An application can invoke #line_join= when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- line_join the style of line-join.
appends a path from the current point to the specified point.
An application can invoke #line_to when the #graphics_mode of
the page is in GMode::PathObject.
- x, y the end point of the path
gets the current line width of the page. It returns the current line width for path painting of the page. Otherwise it returns 1.
sets the width of the line used to stroke a path.
An application can invoke #line_width= when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- line_width the width of line.
calculates the byte length which can be included within the specified width.
- text the text to get the width for.
- width The width of the area to put the text.
- word_wrap When there are three words of
"ABCDE FGH IJKL", and the substring until"J"can be included within the width, if word_wrap parameter isfalseit returns12, and if word_wrap parameter isfalseword_wrap parameter isfalseit returns10(the end of the previous word).
measures the passed text width using the current font and font size.
An application can invoke #measure_text_width when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::TextObject.
moves the current text position to the start of the next line with
using specified offset values. If the start position of the current
line is (x1, y1), the start of the next line is (x1 + x, y1 + y).
An application can invoke #move_text_pos when the #graphics_mode of
the page is in GMode::TextObject.
- x, y the offset of the start of the next line.
starts a new subpath and move the current point for drawing path,
#move_to sets the start point for the path to the point (x, y)
and changes the graphics mode to GMode::PathObject.
An application can invoke #move_to when the #graphics_mode of the
page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::PathObject.
- x, y the start point for drawing path
moves the current text position to the start of the next line.
If the start position of the current line is (x1, y1), the start
of the next line is (x1, y1 - text leading).
An application can invoke #move_to_next_line when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::TextObject.
NOTE: Since the default value of Text Leading is 0, an application
has to invoke #text_leading= before #move_to_next_line to set
text leading.
changes the current text position, using the specified offset values.
If the current text position is (x1, y1), the new text position will
be (x1 + x, y1 + y). Also, the text-leading is set to -y.
An application can invoke #move_text_pos when the #graphics_mode of
the page is in GMode::TextObject.
- x, y the offset of the start of the next line.
create path at given coordinates and yields the block closes the path at the end and returns the result of the block
appends a rectangle to the current path.
An application can invoke #rectangle when the #graphics_mode of
the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::PathObject.
returns the current value of the page's filling color. #rgb_fill is valid
only when the page's filling color space is ColorSpace::DeviceRgb.
returns the current value of the page's stroking color. #rgb_stroke is
valid only when the page's stroking color space is ColorSpace::DeviceRgb.
sets rotation angle of the page.
- angle Specify the rotation angle of the page. It must be a multiple of 90 Degrees.
sets the filling color.
An application can invoke #set_cmyk_fill when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- c, m, y, k the level of each color element. They must be between 0 and 1.
sets the stroking color.
An application can invoke #set_cmyk_stroke when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- c, m, y, k the level of each color element. They must be between 0 and 1.
Sets the line dash pattern in the page. An application can invoke
#set_dash when the #graphics_mode of the page is in
GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- pattern pattern of dashes and gaps used to stroke paths, can have at most 8 elements.
- phase the phase in which the pattern begins (default is 0).
Samples of the dash pattern:
set_dash []
set_dash [3], phase: 1
set_dash [7, 3], phase: 2
set_dash [8, 7, 2, 7]
sets the type of font and size leading.
An application can invoke #set_font_and_size when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or
GMode::TextObject.
sets the filling color.
An application can invoke #set_rgb_fill when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- r, g, b the level of each color element. They must be between 0 and 1.
sets the stroking color.
An application can invoke #set_rgb_stroke when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- r, g, b the level of each color element. They must be between 0 and 1.
changes the size and direction of a page to a predefined size.
- size Specify a predefined page-size value. The following values are available.
- direction Specify the direction of the page.
configures the setting for slide transition of the page.
- style the transition style.
- disp_time the display duration of the page. (in seconds)
- trans_time the duration of the transition effect. Default value is 1 (second).
#set_text_matrix sets a transformation matrix for text to be drawn
in using #show_text.
- a the horizontal rotation of the text. Typically expressed as cosine(Angle)
- b the vertical rotation of the text. Typically expressed as sine(Angle)
- c, d ?? appear to be controlling offset adjustments after text drawn ???
- x the page x coordinate
- y the page y coordinate
If the parameter a or d is zero, then the parameters b or c cannot be zero.
Text is typically output using the #show_text function. The function
#text_rect does not use the active text matrix.
An application can invoke #set_text_matrix when the #graphics_mode of
the page is in GMode::TextObject.
prints the text at the current position on the page.
An application can invoke #show_text when the #graphics_mode of the
page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- text the text to print.
moves the current text position to the start of the next line,
then prints the text at the current position on the page.
An application can invoke #show_text_next_line when the
graphics mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or
GMode::TextObject.
moves the current text position to the start of the next line,
then sets the word spacing, character spacing and prints the
text at the current position on the page.
An application can invoke #show_text_next_line_ex when the
graphics mode of the page is in GMode::TextObject.
paints the current path.
An application can invoke #stroke when the #graphics_mode of the
page is in GMode::PathObject or GMode::ClippingPath.
And it changes the graphics mode to GMode::PageDescription.
returns the current value of the page's stroking color space.
table creates a table at the given rect and yields the block in the context of the created table.
- line_width changes the line with of the drawn cells
- spacing spacing between the cells, by default there is no spacing
- fixed_row_height allows to specify the row height instead of calculation
table creates a table at the given coordinates and yields the block in the context of the created table.
- line_width changes the line with of the drawn cells
- spacing spacing between the cells, by default there is no spacing
- fixed_row_height allows to specify the row height instead of calculation
ends a text object. An application can invoke #text_end
when the #graphics_mode of the page is in GMode::TextObject.
And it changes the graphics mode to GMode::PageDescription.
sets the text leading (line spacing) for text showing.
The initial value of leading is 0.
An application can invoke #text_leading= when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or
GMode::TextObject.
prints the text on the specified position.
An application can invoke #text_out when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::TextObject.
- x, y the point position where the text is displayed.
- text the text to show.
print the text inside the specified region. Some chars may not
in the displayed in the space, the number of displayed chars is
returned.
An application can invoke #text_rect when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::TextObject.
- left, top, right, bottom coordinates of corners of the region to output text.
- text the text to show.
- align the alignment of the text.
see #text_rect.
sets the text rendering mode.
The initial value of text rendering mode is TextRenderingMode::Fill.
An application can invoke #text_rendering_mode= when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
moves the text position in vertical direction by the amount of value.
Useful for making subscripts or superscripts.
An application can invoke #text_rise= when the graphics
mode of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- value text rise, in user space units.
gets the width of the text in current fontsize, character spacing and word spacing.
changes the width of a page.
- w Specify the new width of a page. The valid value is between 3 and 14400.
sets the word spacing for text showing.
The initial value of word spacing is 0.
An application can invoke #word_space= when the #graphics_mode
of the page is in GMode::PageDescription or GMode::TextObject.
- value the value of word spacing.